题目
输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
解答1[Java]:使用栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.add(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty())
ret.add(stack.pop());
return ret;
}
}
|
解答2[Java]:使用头插法重建链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
while (listNode != null) {
ListNode temp = listNode.next;
listNode.next = head.next;
head.next = listNode;
listNode = temp;
}
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
head = head.next;
while (head != null) {
ret.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
return ret;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
|
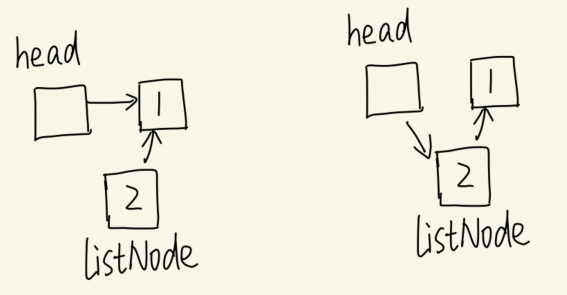
头插法的关键部分
1
2
| listNode.next = head.next;
head.next = listNode;
|
示意图如下:
![head_insert_demo]()
解答3[Java]:递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (listNode != null) {
ret.addAll(printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next));
ret.add(listNode.val);
}
return ret;
}
}
|
递归算法有可能导致函数调用栈溢出。